Description
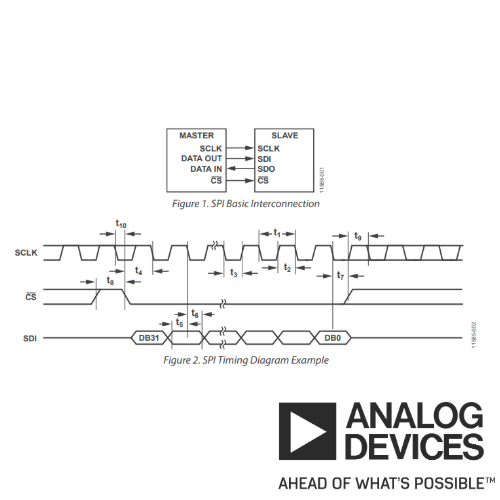
The SPI bus interface is extensively employed for synchronous data transmission due to its ability to support relatively high transmission rates with versatile configurations.
While the SPI has attained de facto standard status, it lacks de jure standardization, meaning it is not officially specified. While this lack of formal specification can be advantageous, allowing designers to optimize functionality, it does introduce complexities in interconnecting different parts.
The SPI bus comprises four unidirectional wires, with varying names for these wires across different parts, even within the same product range.
- Interface enable: CS, SYNC, ENABLE, etc.
- Data in: SDI, MISO (for master), MOSI (for slave), etc.
- Data out: SDO, MISO (for slave), MOSI (for master), etc.
- Clock: SCLK, CLK, SCK, etc.