BHI260AP
Part Number : BHI260AP
ArduinoThe Arduino Nicla Sense ME is an industrial-grade development board packed with Bosch sensors for measuring temperature, humidity, pressure, motion, and gas. Designed for edge computing, it enables advanced data fusion and real-time environmental monitoring. Featuring the BHI260AP smart sensor hub, BMP390 Pressure Sensor, BMM150 Magnetometer, and BME688 environmental sensor, it is ideal for IoT, automation, and smart sensing applications. Additionally, the Arduino ANNA-B112 Evaluation Board, powered by the nRF52832 processor, provides Bluetooth® 5.x (BLE) connectivity, making it a strong complement for wireless communication and RF applications.
ASX00031
Part Number : ASX00031
ArduinoDevelopment Boards & Kits - ARM PRO Portenta Breakoutboard Board
PEC11J-9215F-S0015
Part Number : PEC11J-9215F-S0015
ArduinoPEC11J-9215F-S0015, STM32C011F4 Rotary Encoder Sensor Modulino® Platform Evaluation Expansion Board
MKR1000
Part Number : MKR1000
ArduinoMKR1000 is a powerful board that combines the functionality of the Zero and the Wi-Fi Shield. It is the ideal solution for makers wanting to design IoT projects with minimal previous experience in networking
Arduino Ethernet
Part Number : Arduino Ethernet
ArduinoThe Arduino Ethernet is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328. It has 14 digital input/output pins, 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz crystal oscillator, a RJ45 connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button.
NB: Pins 10, 11, 12 and 13 are reserved for interfacing with the Ethernet module and should not be used otherwise. This reduces the number of available pins to 9, with 4 available as PWM outputs.
An optional Power over Ethernet module can be added to the board as well.
The Ethernet differs from other boards in that it does not have an onboard USB-to-serial driver chip, but has a Wiznet Ethernet interface. This is the same interface found on the Ethernet shield.
An onboard microSD card reader, which can be used to store files for serving over the network, is accessible through the SD Library. Pin 10 is reserved for the Wiznet interface, SS for the SD card is on Pin 4.
The 6-pin serial programming header is compatible with the USB Serial adapter and also with the FTDI USB cables or with Sparkfun and Adafruit FTDI-style basic USB-to-serial breakout boards. It features support for automatic reset, allowing sketches to be uploaded without pressing the reset button on the board. When plugged into a USB to Serial adapter, the Arduino Ethernet is powered from the adapter.
The Revision 3 of the board introduces the standardized 1.0 pinout, that consist in:
added SDA and SCL pins that are near to the AREF pin and two other new pins placed near to the RESET pin, this will the opportunity to shield that use i2c or TWI components to be compatible with all the Arduino boards;
the IOREF that allow the shields to adapt to the voltage provided from the board. Shields that use the IOREF pin will be compatible both with the board that use the AVR, which operate with 5V and with the Arduino Due that operate with 3.3V. Next to the IOREF pin there is a not connected pin, that is reserved for future purposes.
Arduino Yun Mini
Part Number : Arduino Yun Mini
ArduinoArduino Yun Mini is a breadboard PCB developed with ATmega 32u4 MCU and QCA MIPS 24K SoC CPU operating up to 400 MHz. Qualcomm Atheros CPU supports a Linux distribution based on OpenWRT named Linino. The board has built- in WiFi ( IEEE 802.11b/g/n operations up to 150Mbps 1x1 2.4 GHz ) supports 20 digital input/output pins (of which 7 can be used as PWM outputs and 12 as analog inputs), a 16 MHz crystal oscillator, a micro USB connector, an ICSP header, two reset buttons and one user button. The Arduino Yún Mini is similar to the Leonardo in that the ATmega32u4 has built-in USB communication, eliminating the need for a secondary processor. This allows the Arduino Yún Mini to appear to a connected computer as a mouse and keyboard, in addition to a virtual (CDC) serial / COM port.
Arduino MEGA ADK
Part Number : Arduino MEGA ADK
ArduinoThe Arduino MEGA ADK is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560. It has a USB host interface to connect with Android based phones, based on the MAX3421e IC. It has 54 digital input/output pins (of which 15 can be used as PWM outputs), 16 analog inputs, 4 UARTs (hardware serial ports), a 16 MHz crystal oscillator, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button.
The MEGA ADK is based on the Mega 2560.
Similar to the Mega 2560 and Uno, it features an ATmega8U2 programmed as a USB-to-serial converter.
Revision 2 of the Mega ADK board has a resistor pulling the 8U2 HWB line to ground, making it easier to put into DFU mode.
Revision 3 of the board has the following new features:
1.0 pinout: added SDA and SCL pins that are near to the AREF pin and two other new pins placed near to the RESET pin, the IOREF that allow the shields to adapt to the voltage provided from the board. In future, shields will be compatible both with the board that use the AVR, which operate with 5V and with the Arduino Due that operate with 3.3V. The second one is a not connected pin, that is reserved for future purposes.
Stronger RESET circuit.
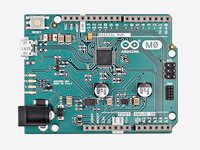
Arduino M0
Part Number : Arduino M0
ArduinoWith the new Arduino M0 board, the more creative individual will have the potential to create one’s most imaginative and new ideas for IoT devices, wearable technologies, high tech automation, wild robotics and other not yet thinkable adventures in the world of makers. The Arduino M0 represents a simple, yet powerful, 32-bit extension of the Arduino UNO platform. The board is powered by Atmel’s SAMD21 MCU, featuring a 32-bit ARM Cortex M0 core. With the addition of the M0 board, the Arduino family becomes larger with a new member providing increased performance.
The power of its Atmel’s core gives this board an upgraded flexibility and boosts the scope of projects one can think of and make; moreover, it makes the M0 the ideal educational tool for learning about 32-bit application development.
A001078
Part Number : A001078
ArduinoARDUINO ROBOT US PLUG; Silicon Manufacturer:Atmel; Silicon Family Name:ATmega; Core Architecture:AVR; Core Sub-Architecture:AVR RISC; Silicon Core Number:ATmega32U4; Kit Contents:Eval Board ATmega32U4; Product Range:-; No. of Bits:8bit
A002078
Part Number : A002078
ArduinoARDUINO ROBOT UK PLUG; Silicon Manufacturer:Atmel; Silicon Family Name:ATmega; Core Architecture:AVR; Core Sub-Architecture:AVR; Silicon Core Number:ATmega32U4; Kit Contents:Eval Board ATmega32U4; Product Range:-; Features:Arduino on Wheels 2 x AVR CPUs Full Color SPI LCD Keypad Prototyping Area 5V USB/AA Battery; No. of Bits:8bit
ABX00031
Part Number : ABX00031
ArduinoNANO 33BLE SENSE DEV BRD, CORTEX-M4F MCU; Silicon Manufacturer:Nordic Semiconductor; No. of Bits:32bit; Silicon Family Name:-; Core Architecture:ARM; Core Sub-Architecture:Cortex-M4F; Silicon Core Number:nRF52840; Product Range:- RoHS Compliant: Yes
SAM3X
Part Number : SAM3X
ArduinoATSAM3X8E Arduino Due AT91SAM3 ARM® Cortex®-M3 MCU 32-Bit Embedded Evaluation Board
050-103
Part Number : 050-103
ArduinoW5500 Ethernet Interface Arduino Platform Evaluation Expansion Board
AKX00027
Part Number : AKX00027
ArduinoArduino, Explore IoT Kit, Product Name: Arduino Explore IoT Kit, Kit Classification: Development Kit, Processor Part Number: AKX00027
TJA1049T/3J
Part Number : TJA1049T/3J
ArduinoMAX31855KASA+T, MAX31865ATP+T, SP335ECR1-L, TJA1049T/3J Arduino Portenta Machine Control - Embedded Evaluation Board
AKX00032
Part Number : AKX00032
ArduinoArduino, Portenta Machine Control, Product Name: Arduino Portenta Machine Control, Kit Classification: Development Kit, MPN: AKX00032